| SPA
Ferrite Domen
Absorbing Microwave Ferrite Materials
Absorption of microwave energy by
ferrite is based on harnessing the natural ferromagnetic resonance of
this material.
There types of ferrite powder were developed to be used as fillers
dispersed in resins, rubbers, and paints featuring microwave energy
absorption capability.
Operation frequency of these materials depends on grain size and
properties of ferrite powders used in their fabrication. Relatively thin
tiles and other covering media can be formed combining layers of all
three types of materials resulting in different electric conductivity of
absorbing body.
|
Type
of absorber
|
Absorbing
material base
|
Operating
frequency bandwidth
GHz
|
Degree
of electric conductivity
|
|
PM
|
Mn-Zn
ferrite powders
|
1-
5
|
high
|
|
PG
|
Mg
ferrite powders
|
1-20
|
poor
|
|
PH
|
Hexaferrite
powders
|
1-40
|
poor
|
|
CH
|
Hexaferrite,
ceramic version
|
1-40
|
medium
|
Forms and Dimensions
STANDARD FORM AND DIMENSIONS OF
MICROWAVE FERRITE PARTS
Ferrite parts can be delivered both as fired or machined articles.
Shapes
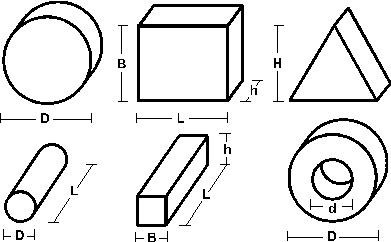
Parts as fired, dimensions (mm)
|
|
Disks
|
Plates
(square, rectangle, triangle)
|
Round
and square
cross-section rods
|
Rings
|
|
D
|
10
120
|
|
5
40
|
5
100
|
|
L
|
|
15
120
|
20
120
|
|
|
B
|
|
5
60
|
5
30
|
|
|
H
|
|
<
90
|
|
|
|
h
|
3
10
|
3
10
|
5
15
|
2.5
15
|
|
d
|
|
|
|
2
70
|
Standard tolerances: ± (3
4)%
Machined parts are to be delivered in
accordance with the Customers drawings.
Standard tolerances: ±0.02 mm
Standard finish: Ra =0.6 mm
Symbols
|
4pMs
|
Saturation
magnetization
|
Gauss
|
|
DH
|
FMR
linewidth
|
Oe
|
|
e'
|
Dielectric
constant
|
|
|
tgde
|
Dielectric
loss tangent
|
|
|
geff
|
Lande
factor
|
|
|
Tc
|
Curie
temperature
|
oC
|
|
DHk
|
Spin
wave linewidth
|
Oe
|
|
Hc
|
Coercive
force
|
Oe
|
|
Br
|
Remanent
flux density
|
Gauss
|
|
HAeff
|
Effective
anizotropy field
|
Oe
|
|
r
|
Density
|
g/cm3
|
|